はじめに
近年、業務アプリケーションにAI機能を組み込む事例が急速に増えています。しかし、AIの出力は本質的に不確実性を含むため、従来のWebアプリケーション開発で重視されてきた型安全性や保守性を維持することが課題となっています。
本記事では、InstructorライブラリとClean Architectureを組み合わせることで、型安全で保守性の高いAI統合パターンを実現する方法を紹介します。特に、複雑な業務ロジックを持つアプリケーションでAIを活用する際の自分なりに考えたベストプラクティスに焦点を当てます。
技術スタックと全体設計
使用技術
- @instructor-ai/instructor: 構造化されたAI出力を型安全に処理
- OpenAI API: 大言語モデルとしてGPT-4.1やgeminiを使用
- Zod: スキーマ定義とバリデーション
- TypeScript: 型安全性の担保
- Clean Architecture: レイヤー分離とドメイン中心設計
アーキテクチャ概要
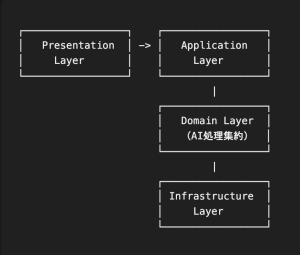
核心的な設計パターン
1. ドメインエンティティでのAI処理カプセル化
AI処理に関する全ての責任をドメインエンティティに集約することで、業務ロジックとAI処理の結合度を高め、外部からの依存関係を最小限に抑えます。
2. 統一インターフェースによる標準化
型定義の詳細
// AI実行コンテキストの型定義
export interface AIExecutionContext {
userInput: string;
attachedFileUrls?: string[];
previousResults?: Record<string, any>;
sessionContext?: Record<string, any>;
}
// AI設定の型定義
export interface AIConfig {
model: string; // 使用するモデル名
temperature: number; // 生成の創造性(0-1)
max_retries: number; // 最大リトライ回数
timeout: number; // タイムアウト(ミリ秒)
}
// AI処理可能エンティティの統一インターフェース
export interface AIProcessableEntity {
/**
* AI出力の構造を定義するZodスキーマを取得
* @returns AI出力をバリデーションするためのZodスキーマ
*/
getZodSchema(): z.ZodSchema<any>;
/**
* AI処理用のプロンプトを生成
* @param context AI実行コンテキスト
* @returns 生成されたプロンプト文字列
*/
generatePrompt(context: AIExecutionContext): string;
/**
* AI処理の設定を取得
* @returns AI処理に使用する設定オブジェクト
*/
getAIConfig(): AIConfig;
/**
* AI処理用のコンテキストを構築
* @param context AI実行コンテキスト
* @returns AI処理に使用するコンテキスト文字列
*/
getContextForAI(context: AIExecutionContext): string;
/**
* AI出力をパースしてエンティティの状態を更新
* @param aiResponse AI APIからのレスポンス
* @param userInput ユーザーからの入力
* @param attachedFileUrls 添付ファイルのURL配列
*/
parseFromAIResponse(
aiResponse: any,
userInput: string,
attachedFileUrls?: string[]
): void;
}
3. 実装例:ビジネス分析エンティティ
// ビジネス推奨事項の出力型定義
export interface BusinessAnalysisResponse {
recommendations: Array<{
id: string;
title: string;
description: string;
priority: number;
reasoning: string;
}>;
metadata: {
analysisApproach: string;
keyInsights: string[];
confidence: number;
};
}
// 統一インターフェースを実装したビジネス分析エンティティ
export class BusinessAnalysisEntity implements AIProcessableEntity {
private recommendations: BusinessAnalysisResponse['recommendations'] = [];
private metadata?: BusinessAnalysisResponse['metadata'];
private userInput = '';
private attachedFiles: string[] = [];
getZodSchema(): z.ZodSchema<BusinessAnalysisResponse> {
return z.object({
recommendations: z.array(
z.object({
id: z.string().describe("推奨項目ID"),
title: z.string().min(5).max(100).describe("推奨タイトル"),
description: z.string().min(50).max(300).describe("詳細説明"),
priority: z.number().min(1).max(5).describe("優先度"),
reasoning: z.string().min(20).max(200).describe("推奨理由")
})
).min(3).max(8).describe("ビジネス推奨項目"),
metadata: z.object({
analysisApproach: z.string().describe("分析アプローチ"),
keyInsights: z.array(z.string()).describe("主要な洞察"),
confidence: z.number().min(0).max(1).describe("信頼度")
}).describe("メタデータ")
});
}
generatePrompt(context: AIExecutionContext): string {
return `
あなたはビジネス分析の専門家です。
## コンテキスト
ユーザー入力: ${context.userInput}
添付ファイル: ${context.attachedFileUrls?.join(', ') || 'なし'}
前回結果: ${JSON.stringify(context.previousResults) || 'なし'}
## 指示
以下の要件に基づいて、構造化された推奨事項を提供してください
## 出力要件
- 実行可能で具体的な推奨事項を提供してください
- 各推奨事項には明確な根拠を示してください
- 優先度付けを行い、実装の優先順位を明確にしてください
`;
}
getAIConfig(): AIConfig {
return {
model: "gpt-4",
temperature: 0.1,
max_retries: 3,
timeout: 30000
};
}
getContextForAI(context: AIExecutionContext): string {
return `
ユーザー入力: ${context.userInput}
添付ファイル: ${context.attachedFileUrls?.join(', ') || 'なし'}
前回結果: ${JSON.stringify(context.previousResults) || 'なし'}
`;
}
parseFromAIResponse(
aiResponse: BusinessAnalysisResponse,
userInput: string,
attachedFileUrls?: string[]
): void {
// AIレスポンスの検証
const schema = this.getZodSchema();
const validated = schema.parse(aiResponse);
// エンティティの状態を更新
this.recommendations = validated.recommendations;
this.metadata = validated.metadata;
this.userInput = userInput;
this.attachedFiles = attachedFileUrls || [];
}
// 追加のドメインメソッド
getPublicResult() {
return {
recommendations: this.recommendations,
metadata: this.metadata
};
}
}
4. 型安全なAIサービス層
ドメインエンティティとInstructorクライアントを橋渡しする統合サービス層を実装します。
export class UnifiedAIService {
constructor(
private instructorClient: InstructorClient,
private logger: Logger
) {}
async processWithEntity<T>(
entity: AIProcessableEntity,
context: AIExecutionContext
): Promise<T> {
try {
const prompt = entity.generatePrompt(context);
const schema = entity.getZodSchema();
const config = entity.getAIConfig();
const result = await this.instructorClient.chat.completions.create({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: prompt }],
model: config.model,
temperature: config.temperature,
max_retries: config.max_retries,
response_model: {
schema: schema,
name: `${entity.constructor.name}Response`
}
});
// エンティティの状態を更新
entity.parseFromAIResponse(
result,
context.userInput,
context.attachedFileUrls
);
return result as T;
} catch (error) {
this.logger.error('AI processing failed', {
error,
entity: entity.constructor.name
});
throw new AIProcessingError('AI処理に失敗しました', error);
}
}
}
実装のメリット
1. 型安全性の実現
ZodスキーマとTypeScript型定義の組み合わせにより、AI出力からアプリケーション内での利用まで、一貫した型安全性を実現できます。
// AI処理の結果は完全に型安全
const result: BusinessAnalysisResponse = await aiService.processWithEntity(
entity,
context
);
// IDEで型補完が効く
console.log(result.recommendations[0].title); // ✅ 型安全
console.log(result.invalidProperty); // ❌ コンパイルエラー
2. コンテキストに応じた柔軟な処理
実行コンテキストに含まれる情報(ユーザー入力、添付ファイル、前回結果など)に応じて、プロンプトを動的に調整できます。
const context: AIExecutionContext = {
userInput: "売上を向上させる方法を教えて",
attachedFileUrls: ["<https://example.com/sales-data.xlsx>"],
previousResults: { lastAnalysis: "marketing focus needed" }
};
// コンテキストの情報がプロンプトに自動的に反映される
const prompt = entity.generatePrompt(context);
3. テスタビリティの向上
各ドメインエンティティが自己完結的にAI処理を管理するため、モックを使った単体テストが容易になります。
describe('BusinessAnalysisEntity', () => {
it('should generate appropriate schema', () => {
const entity = new BusinessAnalysisEntity();
const schema = entity.getZodSchema();
expect(schema.shape.recommendations).toBeDefined();
expect(schema.shape.metadata).toBeDefined();
});
it('should parse AI response correctly', () => {
const entity = new BusinessAnalysisEntity();
const mockResponse: BusinessAnalysisResponse = {
recommendations: [
{
id: "1",
title: "テスト推奨",
description: "テスト用の推奨事項です。詳細な説明を含んでいます。",
priority: 3,
reasoning: "テスト目的のため"
}
],
metadata: {
analysisApproach: "テスト分析",
keyInsights: ["洞察1"],
confidence: 0.8
}
};
entity.parseFromAIResponse(mockResponse, "テスト入力");
const result = entity.getPublicResult();
expect(result.recommendations).toHaveLength(1);
expect(result.metadata?.confidence).toBe(0.8);
});
});
4. 拡張性とメンテナンス性
新しいAI処理が必要になった場合、既存のコードに影響を与えることなく、新しいドメインエンティティを追加するだけで対応できます。
// 新しい業務要件の出力型定義
export interface RiskAnalysisResponse {
analysis: {
summary: string;
riskLevel: 'low' | 'medium' | 'high';
recommendations: string[];
};
actionItems: Array<{
id: string;
action: string;
deadline: string;
assignee?: string;
}>;
}
// 新しい業務要件に対応するエンティティ
export class RiskAnalysisEntity implements AIProcessableEntity {
getZodSchema(): z.ZodSchema<RiskAnalysisResponse> {
return z.object({
analysis: z.object({
summary: z.string().min(50).max(500).describe("分析サマリー"),
riskLevel: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']).describe("リスクレベル"),
recommendations: z.array(z.string()).min(1).max(10).describe("推奨事項")
}).describe("分析結果"),
actionItems: z.array(
z.object({
id: z.string().describe("アクション項目ID"),
action: z.string().min(10).max(200).describe("実行すべきアクション"),
deadline: z.string().describe("期限"),
assignee: z.string().optional().describe("担当者")
})
).min(1).max(20).describe("アクション項目")
});
}
generatePrompt(context: AIExecutionContext): string {
return `
あなたは経営戦略アドバイザーです。
## 分析対象
${context.userInput}
## 出力要件
- リスクレベルを適切に評価してください
- 具体的で実行可能なアクション項目を提案してください
- 期限は現実的な範囲で設定してください
`;
}
getAIConfig(): AIConfig {
return {
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
temperature: 0.2,
max_retries: 5,
timeout: 45000
};
}
getContextForAI(context: AIExecutionContext): string {
return `
ユーザー入力: ${context.userInput}
添付ファイル: ${context.attachedFileUrls?.join(', ') || 'なし'}
セッション情報: ${JSON.stringify(context.sessionContext) || 'なし'}
`;
}
parseFromAIResponse(
aiResponse: RiskAnalysisResponse,
userInput: string,
attachedFileUrls?: string[]
): void {
const schema = this.getZodSchema();
const validated = schema.parse(aiResponse);
// エンティティ固有の状態更新ロジック
// ... 実装詳細
}
}
エラーハンドリングとリトライ機能
Instructorライブラリの自己修正機能と組み合わせて、堅牢なエラーハンドリングを実装します。
export class AIErrorHandler {
async handleAIProcessing<T>(
processingFn: () => Promise<T>,
entity: AIProcessableEntity,
context: AIExecutionContext
): Promise<T> {
try {
return await processingFn();
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof ValidationError) {
// スキーマ検証エラーの場合
this.logger.warn('Schema validation failed, retrying with adjusted prompt', {
entity: entity.constructor.name,
error: error.message
});
throw new AIValidationError('AI出力の形式が不正です', error);
} else if (error instanceof RateLimitError) {
// レート制限エラーの場合
await this.waitForRateLimit();
throw new AIRateLimitError('API利用制限に達しました', error);
} else {
// その他のエラー
throw new AIProcessingError('AI処理中にエラーが発生しました', error);
}
}
}
private async waitForRateLimit(): Promise<void> {
const waitTime = Math.random() * 5000 + 1000; // 1-6秒のランダム待機
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, waitTime));
}
}
まとめ
本記事で紹介したパターンを採用することで、以下の利点を得られます:
- 型安全性: AI出力からアプリケーション全体まで一貫した型安全性
- 保守性: ドメインエンティティによる責任の明確化
- 拡張性: 統一インターフェースによる新機能の追加容易性
- テスタビリティ: 各コンポーネントの独立性によるテストの簡素化
- 再利用性: 標準化されたパターンによる他プロジェクトへの適用
- 柔軟性: コンテキストに応じた動的なプロンプト生成
複雑な業務アプリケーションにAIを統合する際は、単純にAPIを呼び出すだけでなく、アーキテクチャレベルでの設計を慎重に検討することが重要です。Instructorライブラリと適切なアーキテクチャパターンの組み合わせにより、保守性と拡張性を両立したAI統合が実現できます。
